The Diagrams Below Show how Houses Can Be Protected in Areas That Are Prone to Flooding. Summarise the Information by Selecting and Reporting the Main Features, and Make Comparisons Where Relevant.
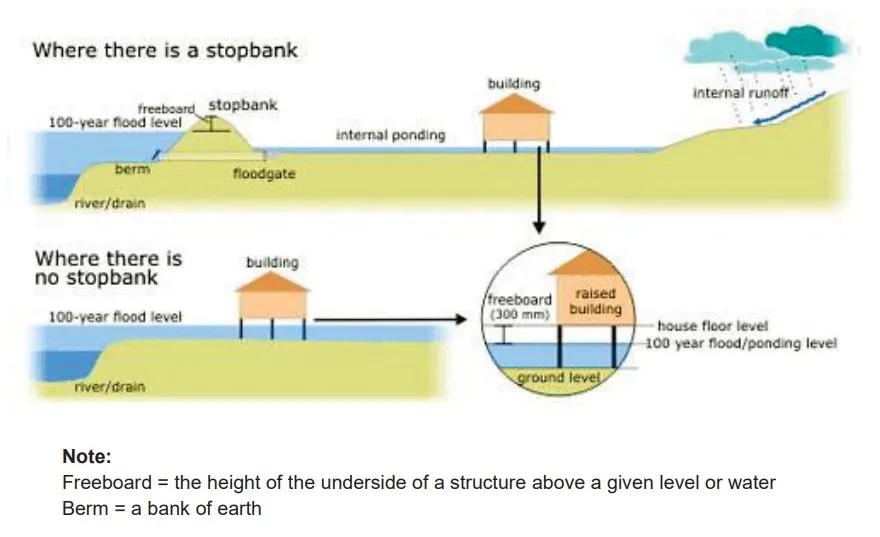
The process diagram illustrates the methods of protesting buildings in regions predisposed to flooding. Overall, it can be seen that stopbank may and may not be utilised to prevent floods.
To begin, where there is a stopbank, internal runoff from heavy downpours of rain is flooded toward the house area. The construction of houses was raised to a standard height to allow internal ponding.
Next, at the junction of the stopbank is a floodgate that controls the inward and outward flow of water. Following this, the freeboard is situated at the stopbank’s point, which permits a 100-year flood level. Then berm allows easy river drainage without causing the house’s collapse.
Converse, where there is no stop bank, houses are constructed with a freeboard of 300mm height and are adequately raised above the ground level. After this, 100 years flood level is achieved, thus preventing the house from being pulled down by the flood. The water is then drained toward the riverside.
Follow Us on IELTSDATA Twitter